Home Profile
Profile  Product Range
Product Range Industries
Industries Infrastructure
Infrastructure Our Quality
Our Quality Custom Manufacturing
Custom Manufacturing Network
Network Contact Us
Contact Us Send Enquiry
Send Enquiry



Basic Dyes
Basic dye is a stain that is cationic (+ve charged) and so will react
with material that is (-ve) negatively charged. This dye is usually
synthetic, that act as bases, and which are actually aniline dyes. Their
color base is not water soluble but can be made so by converting the base
into a salt. The basic dyes, while possessing great tinctorial strength and
brightness, are not generally light-fast.
At the chemical level, basic dyes are typically cationic or positively
charged. Basic dyes display cationic functional groups like -NR3+ or =NR2+.
Since basic dye is a stain that is cationic or positively charged and it is
the reason that it reacts well with material that is anionic or negatively
charged.
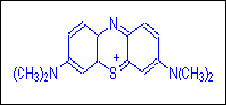
Basic dyes consists of amino groups, or alkylamino groups, as their
auxochromes. Synthetic dye that was discovered by Perkin incidentally was a
basic dye. Few examples of basic dyes are the following, methylene blue,
crystal violet, basic fuchsin safranin, etc. An example of a basic dye that
has amino groups as their auxochrome is pararosanilin or basic red 9
(according to the strict color index system of classification) example of
alkylamino groups is methylene blue or basic blue 9. Basic Blue 9 is a very
popular dye that has vast use. Table given below provides more information
about Basic Blue 9:
| Common name |
Methylene Blue |
| Other name |
Methylene Blue |
| Suggested name |
Swiss blue |
| C I name |
Basic blue 9, Solvent blue 8 |
| C I number |
52015 |
| Ionisation |
Thiazin |
| Solubility aqueous |
3.55% |
| Solubility ethanol |
1.48% |
| Class |
Basic |
| Color |
Blue |
| Empirical formula |
C16H18N3SCl |
| Formula weight |
319.9 |
Yes! I am Interested
Advantages of Basic Dyes
- Moderate substantivity
- Relatively economical
- High Tinctorial strength
- Wide shade range
- Shows good brightness
- Includes some of the most brilliant synthetic dyes
Limitations of Basic Dye
- High acid content
- Colored backwaters
- Poor shade stability
- Preferential dyeing
- Very poor light fastness
Modified Basic Dye
Modified basic dyes have similar chemistry, as of
basic dyes. These only show a bit longer molecular structures than the
typical conventional basic dyes, thus resulting in significantly improved
properties.
Key advantages over conventional basic dyes:-
- Better Lightfastness
- Clear backwaters
- Covers all fibres
- Excellent substantivity
Application of the Basic Dyes
Basic dyes are extensively used for dyeing of
jute, cut flowers, dried flower, coir, etc. For dyeing Acrylic Fibres, basic
dyes are used widely. Modified basic dyes are used for dyeing of Acrylic
Fibre, because these are perfect for this material. If the reason behind the
success of Basic dyes is analysed, it would be seen that the positively
charged cations of the Basic dyes gets attracted towards the negatively
charged anions in the acrylic fibre. Acylic polymers have anionic groups
attached to it. They are most commonly the sulphonate group, -SO3-, followed
closed by the carboxylate group, -CO2-. This reaction of the cation and
anion results in salt linkages. Basic dye do not show absolutely any
migration in acrylic fibers under normal dyeing conditions.
Basic dyes are also preferred to dye leather, because they can get combined
easily with vegetable-tanned leather thus doing away with mordant. Basic
dyes are also used in the coloring of papers.
Home Profile
Profile
 Product
Range
Product
Range Industries
Industries Infrastructure
Infrastructure Our
Quality
Our
Quality Custom
Manufacturing
Custom
Manufacturing Network
Network Contact
Us
Contact
Us Send
Enquiry
Send
Enquiry

![]() Profile
Profile ![]() Product Range
Product Range![]() Industries
Industries![]() Infrastructure
Infrastructure![]() Our Quality
Our Quality![]() Custom Manufacturing
Custom Manufacturing![]() Network
Network![]() Contact Us
Contact Us![]() Send Enquiry
Send Enquiry


![]()
 Basic dyes consists of amino groups, or alkylamino groups, as their
auxochromes. Synthetic dye that was discovered by Perkin incidentally was a
basic dye. Few examples of basic dyes are the following, methylene blue,
crystal violet, basic fuchsin safranin, etc. An example of a basic dye that
has amino groups as their auxochrome is pararosanilin or basic red 9
(according to the strict color index system of classification) example of
alkylamino groups is methylene blue or basic blue 9. Basic Blue 9 is a very
popular dye that has vast use. Table given below provides more information
about Basic Blue 9:
Basic dyes consists of amino groups, or alkylamino groups, as their
auxochromes. Synthetic dye that was discovered by Perkin incidentally was a
basic dye. Few examples of basic dyes are the following, methylene blue,
crystal violet, basic fuchsin safranin, etc. An example of a basic dye that
has amino groups as their auxochrome is pararosanilin or basic red 9
(according to the strict color index system of classification) example of
alkylamino groups is methylene blue or basic blue 9. Basic Blue 9 is a very
popular dye that has vast use. Table given below provides more information
about Basic Blue 9:![]() Profile
Profile
![]() Product
Range
Product
Range![]() Industries
Industries![]() Infrastructure
Infrastructure![]() Our
Quality
Our
Quality![]() Custom
Manufacturing
Custom
Manufacturing![]() Network
Network![]() Contact
Us
Contact
Us![]() Send
Enquiry
Send
Enquiry