Home Profile
Profile  Product Range
Product Range Industries
Industries Infrastructure
Infrastructure Our Quality
Our Quality Custom Manufacturing
Custom Manufacturing Network
Network Contact Us
Contact Us Send Enquiry
Send Enquiry



Inkjet Dyes
Electronic print processes is widely in demand these days. The growth
of multi color inkjet technology is especially growing in the home and
office segments. A substantial and thriving consumer market for inkjet can
be noticed in packaging, publication, and specialty areas.
Inkjet Dyes are highly concentrated colorants specifically designed for
today’s inkjet markets. Available in wide variety of colors, these
ultra pure dyes are low in chlorides and prepared to meet all standard
criteria for the inkjet industry. Inkjet printing are meticulously produced
using comprehensive purification and filtration processes. The quality of an
inkjet printing is very much influenced by the physico-chemical properties
of printing ink.
Dye inks are prepared by dissolving of the liquid colored dyes into a fluid
carrier. This makes the dyes easy to apply. When it is applied to a paper,
the dyes are absorbed very uniformly so they reflect light very evenly. As
the printing is a high precision job the inkjet dyes need to have superior
quality in terms of colors, physical properties, and stability. Generally
direct, reactive, and acid dyes are used as dyes for Inkjet Ink.
Inkjet dyes are available in both forms powder and liquids.
Yes! I am Interested
Given here is a few of the inkjet dyes that are
available in the powder form along with its characteristics:
| CI Name |
CI Number |
Concentration |
Quality |
Characteristics |
| Reactive Red 180 |
181055 |
100.00% |
Salt-free / RO |
Magenta (standard) |
| Acid Red 52 |
45100 |
400.00% |
Low Salt |
Standard for toning as well as shading |
| Acid Blue 9 |
42090 |
165.00% |
Low Salt |
Cyan (standard) |
| Direct Blue199 |
74190 |
175.00% |
Salt-free / RO |
Greenish blue |
| Acid Yellow 23 |
19140 |
200.00% |
Salt-free / RO |
Red shaded Yellow (standard) |
| Direct Black 168 |
30410 |
165.00% |
Salt-free / RO |
Standard |
| Direct Black 19 |
35255 |
200.00% |
Salt-free / RO |
Standard |
Functioning of the Inkjet dyes
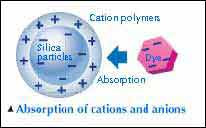
Inkjet
print images use a specific procedure to fix dye firmly for making the
prints durable when they are stored.
Dyes that are generally used for inkjet printers is charged to anionic,
while cationic substances are used as a fixation for the dye.
Inkjet papers that has cationic polymers, have a superlative effect in
fixing the various dyes. As the following diagram illustrates:
Selecting the right powder form Inkjet Dyes
- The powder form inkjet dyes should have a very low salt content.
- There must be the use of latest technologies like Reverse Osmosis in
the desalting process.
- Must possess a very fine particle size.
- The dyes must get easily soluble in water and other types of
co-solvents.
- Gives the right storage options.
- Must be Environment friendly.
- Last but not the least that gets easily converted into liquid "onsite"
Advantages of Inkjet Dyes
Inkjet dyes have many advantages, some are listed
below:
- Stable and soluble.
- Wide array of colors.
- Bright intense colors.
- Wide selection.
Drawbacks of Inkjet Dyes
A few of the drawbacks as experienced by the
users of the inkjet dyes in the printers is given below:
- More damage prone to attacks of sunlight ozone and ultraviolet rays.
- There is a tendency for less stabilization.
- The print is not as much thick as of a pigment based ink.
Comparison between Inkjet Dyes and Inkjet Pigments
Both the materials have different
characteristics. Some pros and cons are listed below:
From the point of view of the manufacturers:
| Dye based Ink |
Pigment Ink |
| As a result of sustained efforts over
the years this technology is now very well mastered in the industry. In
fact Dye based inks started long before the time that inkjet printers
even appeared on the market. |
The technology of pigment is
comparatively difficult to master as the problem of small size of the
particles to create in large quantities must be taken into account. As
nano-sized particles have to be manufactured that will be coated in a
thin resin. This resin is used for protection of the pigment against
external chemical and mechanical attacks. This has a problem too as it
also helps in transportation of the particle inside the ink, through the
nozzles and finally onto the paper. Thus it is quite clear that these
contradictory constraints make this technology a difficult proposition
to perfectly master. |
From the point of view of the manufacturers:-
| Dye Based Ink |
Pigment Ink |
- The dye based ink is usually cheap though the manufacturing cost
is only one factor in ascertaining the selling price of inkjet ink.
- Dye is usually fragile, when exposed to light and Ultra-violet
light, the colored molecules gets broken and loose its color. This
results in the prints to loose their original colors and fades
overtime.
- Ozone and several other common pollutants are also able to
chemically break down the color molecules.
- Drying time has a direct bearing with the drying time of the
solvent on the paper (often this leads to untimely closing of
nozzles, if the ink is set to dry very fast on paper). Consequently,
if the ink and its solvent is not quickly absorbed by the paper,
there is a risk of ink flow or paper deformation.
|
- The Pigment based ink solution gives longevity. It is thus no
surprise that many printers are opting for such pigments.
Manufacturing costs are higher, therefore cost of the ink is higher
to the user.
- Degradation of pigments by pollutants or ozone is not that much,
the presence of the resin coating limiting it further.
- Color density is generally better, or easier to achieve than with
dye-based inks.
- However talking of limitations pigments shows tendency to promote
a defect called bronzing. When brightly lit or if lit with low
incidence, the print can show unpleasant metal-like reflections.
|
Home Profile
Profile
 Product
Range
Product
Range Industries
Industries Infrastructure
Infrastructure Our
Quality
Our
Quality Custom
Manufacturing
Custom
Manufacturing Network
Network Contact
Us
Contact
Us Send
Enquiry
Send
Enquiry

![]() Profile
Profile ![]() Product Range
Product Range![]() Industries
Industries![]() Infrastructure
Infrastructure![]() Our Quality
Our Quality![]() Custom Manufacturing
Custom Manufacturing![]() Network
Network![]() Contact Us
Contact Us![]() Send Enquiry
Send Enquiry


![]()
 Inkjet
print images use a specific procedure to fix dye firmly for making the
prints durable when they are stored.
Inkjet
print images use a specific procedure to fix dye firmly for making the
prints durable when they are stored.![]() Profile
Profile
![]() Product
Range
Product
Range![]() Industries
Industries![]() Infrastructure
Infrastructure![]() Our
Quality
Our
Quality![]() Custom
Manufacturing
Custom
Manufacturing![]() Network
Network![]() Contact
Us
Contact
Us![]() Send
Enquiry
Send
Enquiry